✆ + 1-646-235-9076 ⏱ Mon - Fri: 24h/day
Industry 4.0
In this era, machines, devices, and systems communicate and collaborate seamlessly, providing real-time data that enables factories to become smarter and more efficient.
Key Insights Shaping Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 is all about the digital transformation of industries. It involves the use of technologies such as Big Data, IoT, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence to improve operational efficiency, productivity, and flexibility.
The ability of machines, devices, and systems to communicate with each other is central to Industry 4.0. This interconnectedness allows for real-time data exchange and decision-making, which can optimize processes and reduce downtime.
The use of robots and automated systems is expanding in Industry 4.0, leading to improved efficiency, precision, and safety in manufacturing and other sectors.
These systems combine digital elements with physical processes. They enable real-time monitoring, control, and feedback for more adaptive and responsive industrial operations.
Industry 4.0 can contribute to sustainability efforts by optimizing resource usage, reducing waste, and improving energy efficiency. Smart, data-driven processes can help reduce the environmental footprint of industries.
Industry 4.0 often involves collaboration among various stakeholders, including suppliers, manufacturers, and service providers. These ecosystems are necessary for a seamless digital transformation.
Industry 4.0 Cases
Industrial product development cycle
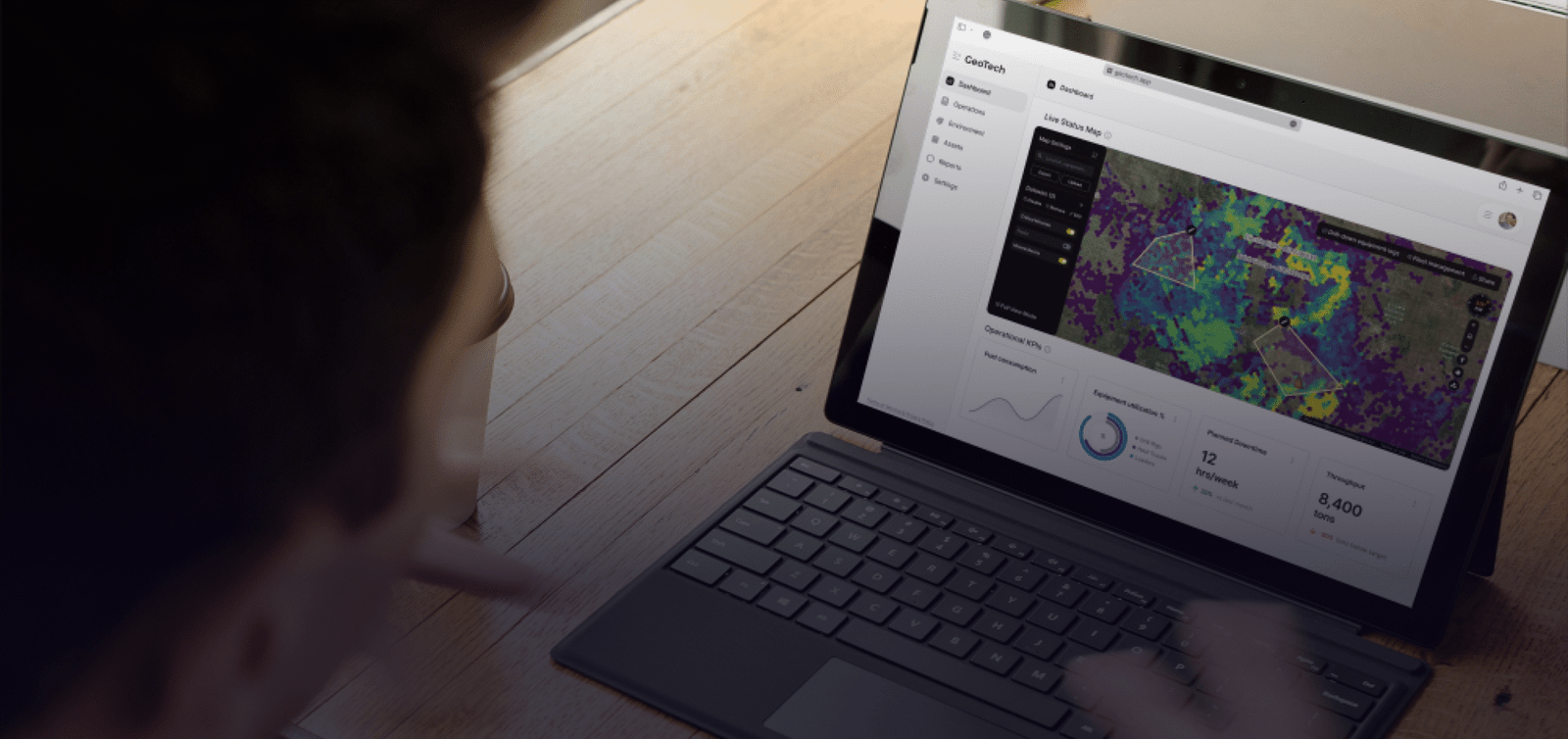
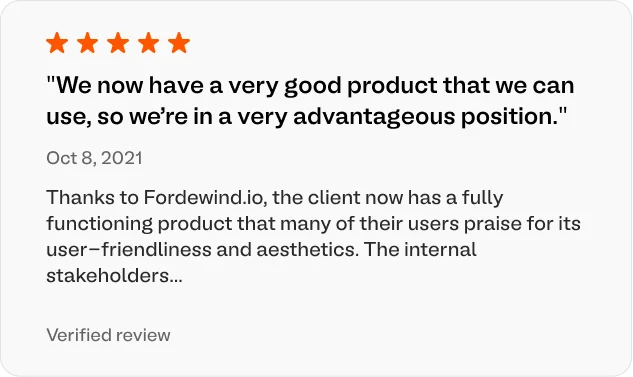
HMI (Human-Machine Interface) generally is industrial-grade touch panel with specific visualization. Special trained personnel by using HMI can control individual units. In today’s industrial landscape, the Human-Machine Interface (HMI) is a critical component that bridges the gap between human operators and complex industrial systems. HMIs are industrial-grade touch panels designed with specific visualizations that allow operators to interact with and control individual units or even entire industrial processes. These interfaces provide an intuitive and user-friendly means for personnel to monitor real-time data, set parameters, and make informed decisions. HMIs are the windows through which humans gain insight into the status and performance of machines, ensuring that operations run smoothly and efficiently. Moreover, they offer a level of control and interactivity that empowers trained personnel to optimize processes, diagnose issues, and maintain the highest levels of productivity and safety.
Edge device is hardware and software platform that controls data flow between internal (industrial) and external(for example internet cloud) networks. Some common functions of edge devices are the processing, monitoring and visualising the specific data (for example KPIs, energy and water consumption) for managers. Edge devices represent a vital layer of the modern industrial network infrastructure. They serve as the hardware and software platforms responsible for managing data flow between the internal industrial networks and external systems, such as the internet or cloud-based platforms. These devices are strategically positioned at the edge of the network to process, monitor, and visualize specific data. Their functions extend beyond mere data transmission; they play a key role in data analytics, helping to extract valuable insights, such as Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and energy or water consumption metrics. Edge devices are essential for managers and decision-makers, as they provide real-time data that can be used to optimize operations, reduce downtime, and enhance resource management. These devices are the first line of defense against data overload and latency, ensuring that relevant data reaches the right personnel when they need it most.
SCADA (supervisory control and data acquisition) is a software application for controlling industrial processes, which is the gathering of data in real time from industrial equipment. Highly qualified staff can monitor and control the whole plant by using SCADA system. Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) is a powerful software application that underpins the control and monitoring of industrial processes. SCADA systems are integral to the gathering of real-time data from a wide array of industrial equipment and sensors. Highly qualified staff use SCADA as a centralized control hub to visualize, analyze, and manage the entire plant or industrial facility. SCADA goes beyond the simple collection of data; it empowers professionals to make informed decisions and take timely actions based on the insights derived from the data. Whether it’s optimizing manufacturing processes, monitoring equipment health, or ensuring compliance with industry standards, SCADA systems play a pivotal role in maintaining operational excellence. These systems are instrumental in enhancing efficiency, reducing operational risks, and ensuring the reliability of industrial processes.
In today’s rapidly evolving industrial landscape, HMIs, Edge Devices, and SCADA systems are integral components in the journey toward automation, efficiency, and data-driven decision-making. They represent the synergy between technology and human expertise, driving the success of industries across the globe.

Industry 4.0 Innovations
Industry 4.0 generates vast amounts of data. Big Data analytics tools and techniques help organizations make sense of this data, providing insights for better decision-making, predictive maintenance, and process optimization.
Edge computing involves processing data closer to the source, reducing latency and enabling real-time decision-making. This is crucial for IoT devices in Industry 4.0 applications.
High-speed, low-latency 5G networks are essential for transmitting data in real-time, especially in applications like autonomous robotics and remote control of machinery.
Blockchain is used for secure, transparent, and traceable transactions and data sharing in supply chains, enabling better trust and verification in the manufacturing and logistics sectors.
AR and VR technologies are used for training, maintenance, and design in Industry 4.0. They provide immersive experiences and can improve productivity.
High-precision sensors are critical in Industry 4.0 for data collection and monitoring. They provide real-time information on equipment performance, quality, and environmental conditions.


Automotive
IoT in the automotive industry connects vehicles to the internet, enhancing safety, efficiency, and the overall driving experience.


Smart Home
Smart home tech connects and controls devices for convenience, efficiency, and security, streamlining daily life.

Healthcare
Our advanced software solutions
revolutionize patient monitoring and health management in the world of digital healthcare.


Smart Hospitality
Elevate the guest experience with Smart IT solutions for hotels, restaurants, and the entire hospitality industry.
Contact Us
New York
348 W. 57th St., New York, NY 10019
+16462359076
contact@fordewind.io
Vancouver, Canada
W Georgia St, Vancouver, Canada
+16047649232
contact@fordewind.io
Warsaw, Poland
Plac Europejski 4, Warsaw, Poland
+48452478282
contact@fordewind.io
Tallinn, Estonia
Kesklinna linnaosa, Kaupmehe, 10114, Estonia
contact@fordewind.io
Kyiv, Ukraine
19 Koval’s’kyi Lane, Kyiv, Ukraine
+380967764322
contact@fordewind.io