Bluetooth Low Energy is implemented into many gadgets that we use today

After studying and successfully applying the transfer of information wirelessly,
there was a need to transfer data using devices with autonomous power supplies. The problem is that another device must work with this device, which incessantly transmits data or listens to the air.
While using the transmitter and receiver powered by batteries, its transmission breaks, and problems arise, which has been solved in a new Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) data transfer protocol to save energy.
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) is part of Bluetooth 4.0, which also includes initial Bluetooth protocols and high-speed Bluetooth. Compared to primarily Bluetooth, BLE is designed to use less power by maintaining a similar range. BLE is a technology that is still out of service and only transfers short amounts of data when necessary. This technology significantly reduces energy consumption, making it ideal for use when a constant and long-term connection with low data rates is required. BLE is perfect for a TV remote control, but not for a wireless media transmission device that requires a lot of data to transfer.
Bluetooth Low Energy is implemented into many gadgets we use today.
From smartphones, smart TVs, advanced technologies such as medical equipment to ordinary devices such as our coffee machines, everyone uses BLE.
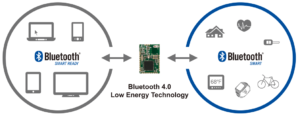
What does BLE provide?
- Provides multiplatform communication: it can be easily transmitted through a large number of devices running Android, iOS, Linux, Windows Phone
- Better pairing speed
- Help keeping in touch for long periods
- Substantially lower implementation costs
- Energy efficiency
The BLE protocol is used in a scenario: rarely transmit data and process for a long time. In particular, it is possible to use dual-mode BLE gadgets in smartphones, tablet PCs, laptops. Single-mode can be used in many fields of activity. Devices from the sections of health, automation, analysis, management fall under these areas.
Many tasks can be solved when other single-level BLE devices are defined within the radius of the two-level module. These devices include signaling devices that notify the owner about the distance from a bag, purse, wallet, portable packaging, and other personal items equipped with a BLE module. These keychains with BLE are excellently used as beacons for a child to prevent losing the device in insufficiently crowded places.
The stable operation and low power consumption of the BLE protocol make it possible to consider it as a replacement for NFC, namely RFID tags. But the option of combined BLE + NFC work looks more attractive. The former gives a large radius, coupled with stable operation, the latter is responsible for the logical pairing, plus provides reliable protection due to a short-range.
This specification is used in smart home systems.
The operation of devices via Bluetooth with low power consumption allows a consumer to open doors and gates remotely and operate other mechanisms from a long distance without changing the battery using a wireless and compact control panel.
Besides, a BLE module implementation into a smartphone that is always at hand allows controlling any devices and accessories of smart home at a decent distance through paired channels. Or to connect to a touch panel for remote control from another room.
BLE looks good in the paper, but what happens in practice?
That is a good question from the point of view of safety. The prob is that BLE is just a protocol. Manufacturers should safely incorporate BLE into their equipment. We know that even the best encryption protocol will not work if the random number generator isn’t random enough. The same goes for BLE. Thus, we can say that the safety of BLE is in the hands of its executives.
While all Bluetooth Low Energy devices have been designed with the main goal of improving user experience, has security been the last in the process?
Let’s look at the three principal vulnerabilities BLE can expose its users to:
Eavesdropping: As the name suggests, listeners refer to a third party device listening to the data exchanged between two coupled devices. A connection between two paired devices means a chain of confidence. The chain gets broken when one of the devices is removed. An attacker may use the device number to access other Bluetooth devices. Even if encryption/decryption keys were removed, an attacker can force the offline PIN using a Bluetooth Sniffer (based on the device ID). Once you have received the PIN, the device can easily be hacked.
Man in the middle (MITM) attacks in the middle involving a third-party device that simulates a legitimate device, striking two legitimate devices to believe that they are connected while legitimate devices are connected to a simulator (the medium). This type of attack allows an attacker/personator to access all data exchanged between devices as well as manipulate the data by deleting or modifying them before they reach the corresponding device.
Denial of Service and Fuzzing Attack. Since most wireless devices currently operate with built-in rechargeable batteries, these devices take on a risk of Service Denial Attacks (DoS). DoS attacks expose the system to frequent failures, leading to complete battery exhaustion. Blurred attacks also cause system crashes, as an attacker may send damaged or non-standard data to the radio of a Bluetooth device and test its response, possibly confusing the device.
To sum up, Bluetooth Low Energy is a protocol specially designed for devices with a limited source of autonomous energy that needs to send information for several days or weeks without recharging. Smartphones, tablet PCs, laptops are equipped with dual-mode BLE modules. Single-mode BLE modules are used in small electronics and accessories such as heart rate meters or proximity keys.
Fordewind.io is an IoT engineering and development company based in Kiev, Ukraine. Our main areas of interest and expertise are the automotive industry and Smart Home/City projects. Contact us right now without a doubt and learn more about how we can help you build the future.